Medical Leave Reflections plus Empathy Sphere Essay
 Good news first, I have a new essay out in Uncanny Magazine, “Expanding Our Empathy Sphere Using F&SF, a History,” where I talk about my term ’empathy sphere’ meaning the collection of beings we consider coequally a person with ourselves, something which historically has expanded over time, and which is useful in thinking about why when we read old utopias, like More’s Utopia, or early SF utopias, they often don’t feel utopian to us anymore if they don’t have freedom for groups that are inside our empathy sphere but weren’t inside More’s (like lower classes, women, certain races, clones, A.I.s etc.). It’s a useful analytic term and one several people have asked me to write about, and I also give a history of how SF has helped expand this sphere over time. I hope you enjoy reading it!
Good news first, I have a new essay out in Uncanny Magazine, “Expanding Our Empathy Sphere Using F&SF, a History,” where I talk about my term ’empathy sphere’ meaning the collection of beings we consider coequally a person with ourselves, something which historically has expanded over time, and which is useful in thinking about why when we read old utopias, like More’s Utopia, or early SF utopias, they often don’t feel utopian to us anymore if they don’t have freedom for groups that are inside our empathy sphere but weren’t inside More’s (like lower classes, women, certain races, clones, A.I.s etc.). It’s a useful analytic term and one several people have asked me to write about, and I also give a history of how SF has helped expand this sphere over time. I hope you enjoy reading it!
Less good and more personal news next, my health has taken a bad turn, bad enough that I have taken medical leave and had to cancel my fall teaching. My medical team is still running tests (U Chicago has an exceptional hospital), and they don’t think it’s life-threatening, but it’s probably a circulatory system issue, with symptoms including severe dizziness, faintness, stumbling & falling, all of which make it very hard to do anything, including teaching. They’re still running tests, and generally hopeful that things will improve, but on a scale of months, not weeks or days. I hope to be well enough to teach in spring. As for writing, I’m doing some, since one of the hard things in this situation is to keep my morale up and nothing nothing nothing makes me happier than writing, but it’s still being slowed, alas, though may pick up a bit as the glut of start-of-leave tasks diminishes.
So I wanted to share some reflections on this.
One is that it is amazing how much of the resistance to taking medical leave came from me, not others. Even when friends, colleagues, disability staff at the university, and family were all encouraging it, even when I confirmed my employer policies meant I could do it w/o a bad hit to income etc., even when I was in the doctor’s office and the doctor checked a couple things and the first words out of her mouth were, “Well, you can’t work!”, even when the doctors took it so seriously they wouldn’t let me walk out of the office but insisted I wait for a wheelchair, I still immediately started protesting about, “Well, if I teach remotely from lying down… but this course is special… but if I have X accommodation…” etc. arguing back even against such reasonable arguments as, “Your body is failing to deliver oxygen to your brain! You know what you need to do anything?! Oxygen for your brain!” Nonetheless, it took many days, much encouragement, and many repetitions of exhaustion & collapses for me to decide that, yes, everyone urging me to take medical leave did indeed mean I should take medical leave. (Important principle: in teaching all courses are special/unique, if you make exceptions for that you’ll never stop making exceptions.)
Where did my resistance to taking medical leave come from, when I was in the extraordinarily fortunate position of my employers, doctors, and family all being 100% supportive? (a rare and lucky thing). Partly it came from not wanting to let others down, partly from not wanting to admit to myself that it was serious, but a big part of it also comes from narratives, from The Secret Garden, from Great Expectations, from a hundred other narratives, some classic some recent, in which chronic illness/weakness/invalidness is all in one’s head, or where it’s “overcome” by force of will or powering through the pain, so that even in the fortunate case where everyone around me was being supportive and great, those narratives of powering through were unconsciously deep inside me feeding my resistance to accepting that my doctors and employer aren’t exaggerating when they say, “Don’t work.” This connects to something I discussed in my second-most-recent Uncanny essay, on the Protagonist Problem, that it’s very important to have a variety of narratives and narrative structures, and it can do real harm if one type of narrative or structure dominates depictions of a topic. Some versions of this have been discussed a lot recently: back pre-Star Trek, when close to 100% of black women depicted on TV were housemaids, it did harm by reinforcing bad stereotypes & expectations; similarly today when a very high percentage of immigrant characters depicted on TV are shown committing crimes, it feeds bad expectations. In the Protagonist Problem essay I argue that it also does harm when a large majority of our stories show the day being saved by individual special (often chosen one or superpowered) heroes, since it feeds a variety of bad impulses, including the expectation that teamwork can’t save the day, and feelings of powerlessness if we don’t feel like heroes; the argument isn’t that protagonist narratives are bad, it’s that protagonist narratives being the vast majority of narratives is bad, because any homogeneity like that is bad, just as it’s important for us to depict many kinds of people being criminals on TV, not a few kinds overrepresented and others erased.

Thus, for disability, we also have a problem that depictions of disability tend to repeat a few stock narratives, not one but three really, which together drown out others and dominate our unconscious expectations. One form is is the disabled/disfigured villain, a holdover from pre-modern ideas about Nature marking evil with visible indicators (and virtue with beauty). Another is a person falling ill and dying, a tragedy, which ends up focusing on the friends and loved ones who help along the way, or who survive. Another is ‘inspiration porn’ (David M. Perry has great discussions of this) which has a few varieties but tends to focus on how heroic an abled person is for helping a disabled person achieve a thing (like Secret Garden where she gets him out of the chair) instead of on the disabled person’s achievements/experience, or to present “Look a disabled person did a thing!” but in a weirdly dehumanizing way, the same way you would write “Look, this monkey can play chess!” All of these make people resistant to accepting the label disabled, since, even though it’s really useful once you have (I had trouble for a long time) we associate it with being morally bad, being doomed, or being helpless and dehumanized.
The disability narrative most relevant in my recent situation, though, are the stories of ‘overcoming’ disability, where a person is either cured (through their own efforts or others’), or works hard and pushes through, so the disability becomes a problem of the past, that has been left behind. This often-repeated narrative (present in fiction and nonfiction) encourages the attitude of seeing disability’s disruptions to life as temporary and surpassable. It means that, when I get a new diagnosis, my first thoughts even this many years into having chronic illness, are always about how long it’ll be until I overcome it, what I need to do to get past it, the expectation that it’ll be normal by spring/summer/December/whatever. This often leads me to delay by weeks or months or longer taking steps to, for example, adapt my home to be more comfortable (like getting a lap desk so I can work lying down), and other changes dependent on expecting the condition to be here to stay. I think, as a culture, we really hate telling stories about illnesses and disabilities that are here to stay.
I remember a conversation with a friend once about a situation where a medication good at treating their particular condition was taken off the market, and the parents of a kid with the condition contacted my friend to ask how to advocate or find other ways to get more of the medication, and the friend had to keep saying no that wont’ work, no you can’t get it, no you really can’t get it, no your doctor can’t write a special note, until finally they asked directly, “So what do we do now?” to which my friend answered, “Accept a lower quality of life.” That phrase crystalized things for me. I think in many ways no ending is scarier for us in narrative than accept a lower quality of life. It isn’t a one-time tragedy like death, we have good narrative tools to write tragedy, and to transition focus to the characters who live on, commemorate, remember. Accept a lower quality of life in a story means losing, giving up, surrendering, all the things we want our brave and plucky characters to never do, and then having to live with every day being that much worse forever. It’s neither a happy ending nor a tragic ending, it’s a discouraging ending, and we rarely tell those stories.

I vividly remember the first story like that I ever met, it was a James Harriot All Creatures Great and Small story, about a man whose family had been coal miners, who really wanted to farm, and bought a farm, and worked tirelessly to do a good job, and was a really nice person and always kind and earnest (unlike a lot of the characters in the stories), but then his cows got sick and James tried everything he could to cure them but it didn’t work, and then the farmer came to tell him, with a calm demeanor, that he was selling the farm and had always promised his father he’d go back to coal mining if “things didn’t work out” (coal mining which in the 1920s-30s meant a much shortened life expectancy as well.) James realizing how huge this was (accept a lower quality of life) despite so many efforts said, “I don’t know what to say,” and the farmer answered, “There’s nothing to say, James. Some you win.” I still tear up just thinking of that scene, the cruel unspoken and some you lose applied to a whole long life-still-to-come, every day of which would be worse, and there was no other way. A big part of modern advancement is about avoiding there being no other way–offering insurance, social safety nets, appropriate grants–but it’s also an important type of story to tell sometimes, and one I really needed some examples of. Why? Because those stories, those phrases in my memory (some you win, and, accept a lower quality of life) are not where I think I am now, I’m still working hard on treatments and therapy etc., but I needed to have them in my palette of expectations of things that could be the case, to help me plan. I needed those at the start of term to get out of the, “But surely it’ll get better in a couple weeks if I work hard,” mindset to the better attitude of, “The doctors don’t know how long this will last, I’d better plan in case it lasts a long time.”
If the only outcomes in our expectations are (A) powering through and it gets better, or (B) death/villainy/helplessness-forever, none of those archetypes will give us the sensible advice that it’s wise to plan long-term just in case there is a long-term thing that impacts quality of life. Because today a lot of those can be addressed with adapting tech/stuff/habits. I put off buying a lap desk for 2.5 months this summer, struggling to work lying down, since I didn’t want to waste the money if I was about to get better. But having a lap desk and turning out not to need it is much better than needing one and grinding on without. I also put off adapting the area around my bed to optimize for work, put off getting the new screen which finally today (Oct 7, I started wanting this in July!) got installed so I can have multiple monitors while lying down. I put off realizing that instead of watching chores pile up expecting to catch up when I got better, the household needed to discuss and make changes to reduce the total load of chores (simpler meals, paper plates, self-watering planters, planning! Also: thank you so much Patreon supporters, you made my new lying-down desk and canes and such possible!!).

The some you win stories are extremely sad and shouldn’t become our dominant narrative, but they need to be in the mix, one color in the color wheel, to help people who do face disability to weigh the odds better, and not think well, in 90% of stories I know the person gets better so probably I’ll get better and this [desk/ screen/ cane/ adaptation] is likely to be a waste of money. Because you now what’s a good thing even if the end of one’s real life story is accept a lower quality of life? Accepting a quality of life that’s only 5% lower instead of 20% lower because you’ve adapted your home/ routine/ desk/ fridge/ breakfast routine etc. to mitigate as much of the negative impact as you can. So here I am in what is probably the best possible lying-down desk, writing and producing more than nothing, but I sure would’ve produced more over the last few months if I’d done this sooner. And I also would’ve been a lot more willing to say “You’re right I should take medical leave,” if I had believed my odds of recovering quickly were, say, 50/50, instead of, as narrative tells me, expecting that if I tried hard it was certain that I’d quickly power through (and that if I didn’t recover quickly that heralded either moral weakness, helplessness, or death, three things our minds work very hard to resist). A broader mix of disability narratives whispering in the back of my unconscious mind, telling me there might be many outcomes and I should plan for many outcomes not just for the best, would have done so much good–that’s why we need variety.
 As a coda to this discussion, chatting about it with Jo Walton, she pointed out that both my examples of accept a lower quality of life stories are nonfiction (Herriott’s fictionalized from real life, the other just real life), and that after she and I first discussed the Herriott story she tried hunting for examples of that kind of story far and wide but basically never found them, that she often found it as “a Caradhras, a mountain you can’t get over so you go under, never the end.” But recently she found several examples in the work of the extremely obscure and neglected Victorian writer Charlotte M. Yonge; it’s great to find one, but also to have confirmation from a voracious reader about how rare such narratives genuinely are.
As a coda to this discussion, chatting about it with Jo Walton, she pointed out that both my examples of accept a lower quality of life stories are nonfiction (Herriott’s fictionalized from real life, the other just real life), and that after she and I first discussed the Herriott story she tried hunting for examples of that kind of story far and wide but basically never found them, that she often found it as “a Caradhras, a mountain you can’t get over so you go under, never the end.” But recently she found several examples in the work of the extremely obscure and neglected Victorian writer Charlotte M. Yonge; it’s great to find one, but also to have confirmation from a voracious reader about how rare such narratives genuinely are.
Now, my other reflection is on academia not disability things.
When I finally decided on taking leave I joked to myself, “For academics, ‘vacation’ means when you do the work you really want to do, and ‘medical leave’ is when you actually vacation.” But the reality is that even medical leave I’ve been finding myself doing minimum four hours of academic work a day, sometimes much more. It has been an interesting chance to see, both which specific parts of academic work absolutely can’t be cancelled or handed off to others, and just on the sheer volume of time that academics are required to give to things which are neither teaching nor research. Letters of recommendation wait for no man, ditto letters for other scholars’ tenure files, and mentoring meetings with Ph.D. students about their urgent deadlines; it’s one thing to set aside one’s own agenda but another to neglect things that other people really depend on. So here I was on full disability leave, with all teaching and research obligations on hold, something my university was quickly able to give, and yet I found myself working intensively from waking until dinnertime and still falling farther and farther behind even when the only work I did was letters of recommendation and inescapable paperwork. In other words, at least when rec letter season is upon us, the paperwork and mentoring parts of academia are pretty close to a full 9-to-5 job even without teaching or research! And that is for someone tenured at U Chicago, one of the most privileged teaching positions in the world, with a light load at a very supportive university.
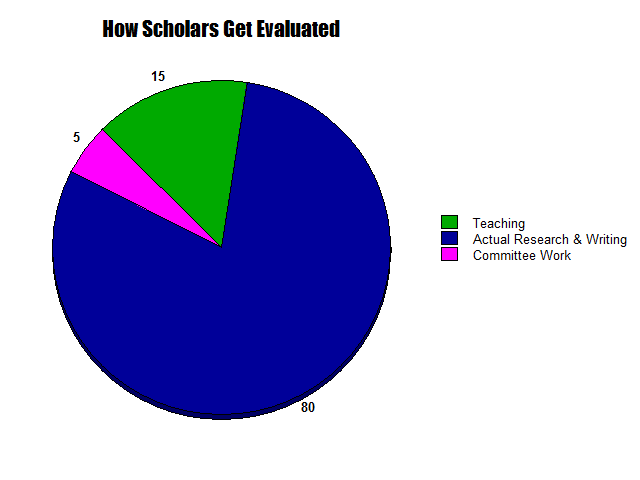
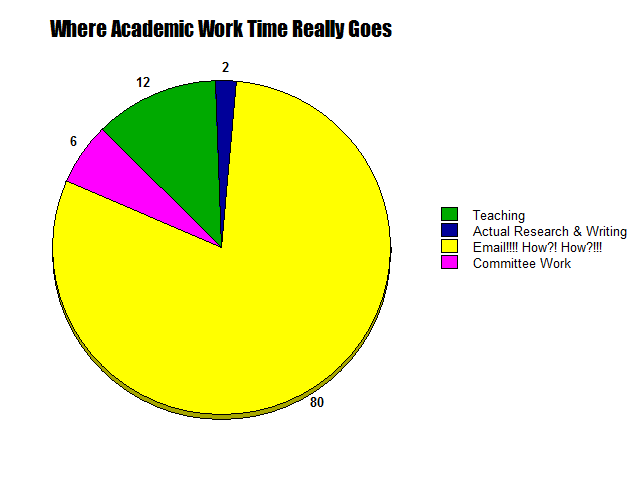
As one friend put it, “I’m not a teacher, I’m a full-time e-mail answerer,” another, “I teach for free, it’s the grading and admin they pay me for,” another, “You can either produce research or keep up with email, but you can’t do both.” We need to factor this in as we think about how academia functions and what reforms to push for, and into how we teach Ph.D. students since things like email skills and time-management skills are absolutely essential to teaching and research when they need to be balanced basically like hobby activities squeezed into the corners of time we can scrape out around the full-time job of admin. It doesn’t have to be this bad. Possibly the problem is best summarized when I was talking to people about a high-level search committee (i.e. hiring at tenured full professor level instead of junior level) and they said they weren’t going to ask for letters of recommendation until they got to the short list of finalists and would only ask for letters for those few, not everyone, “Because we want to respect the time of the important people writing the letters.” Subtext: we don’t respect the time of the less-high-status people writing the many hundreds more letters needed for junior hires. I genuinely think every academic field would produce another 80+ books per year if we just switched to only requesting rec letters for finalists instead of all applicants, and that’s just one example of a small change. In sum, anyone near academia needs to acknowledge that the real pie chart of academic work is depicted below, that we need to plan for that and remember that small changes to self-care or workflow (just studying up on gmail tag and shortcut things for example) can make a huge difference to reducing the unreasonable load and avoiding burnout, and above all that we should always remember that phrase–respect the time of the people doing X–when we plan how to organize things (syllabus, meetings, forms, applications, committees, etc.). And I’m sure a lot of this applies far beyond the academic world as well.
Meanwhile, between recommendation letters I can’t get out of writing, plus disability paperwork, doctor’s appointments, and working on getting my home adapted so my quality of life is diminished by a little instead of a lot in my present state, I’m definitely working-rather-than-resting more than 40 hours a week, and that’s a pretty typical illness experience. It’s good to know that going in, accept it, plan for it, carve out time for the inescapable tasks and to think of adapting the home as time-consuming (or something we should ask for help with!) Otherwise it’s very easy for a week, or month, or three months of ‘rest’ to be not at all restful, and the hoped-for ‘recovery’ to remain elusive. I still have three months of leave before me and I’m definitely leveling up at how to make my leave actually be leave (delegating, adapting things, finding others to write letters when possible) but learning how to make leave actually be leave, and rest actually be rest, is definitely a skill one must level up at, and I think if we understand that it’s a skill (and perhaps tell stories about it?) we’ll be better at realizing we need to actively work to learn it when we (or loved ones) need that skill.
So, for now, I’ll be focusing on rest, and doctor’s appointments, and home adaptation, and things to keep my morale up, and writing (keeps morale up!), and getting ready for the release of Perhaps the Stars (!!!!!!!) but I hope these reflections are helpful, and many thanks to everyone who’s been supportive & helpful throughout. I’ll see you soon when I’m either (A) better or (B) fully adapted to a partly-but-minimally-lower quality of life.
And if you enjoy my writing don’t forget about the Uncanny essay: “Expanding Our Empathy Sphere Using F&SF, a History.”


 As is often the case with this kind of invisible and intermittent disability, the cause of mine is complicated: for me it’s a combination of
As is often the case with this kind of invisible and intermittent disability, the cause of mine is complicated: for me it’s a combination of 

